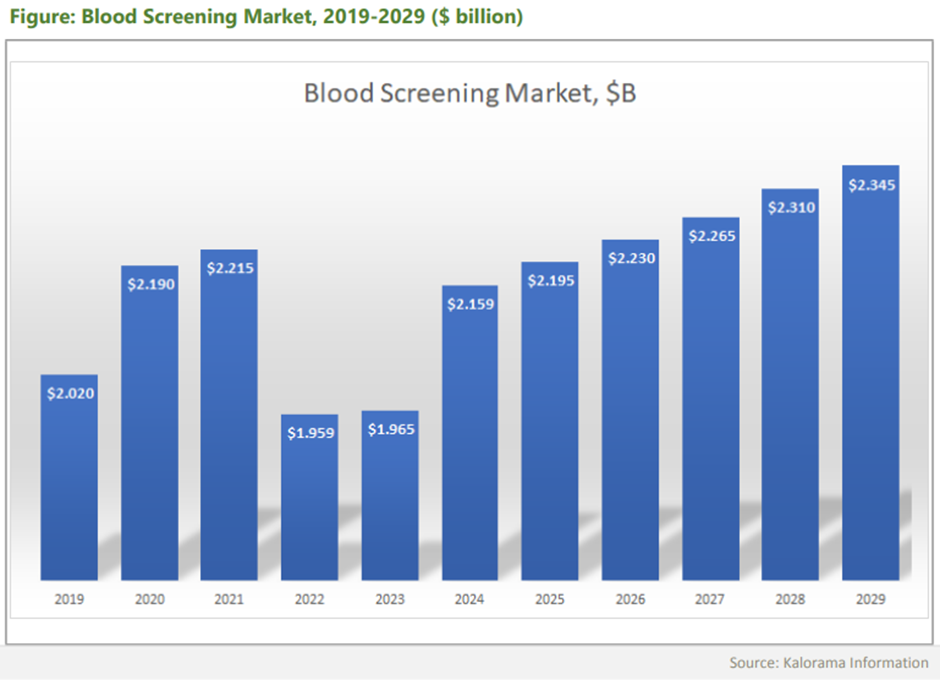
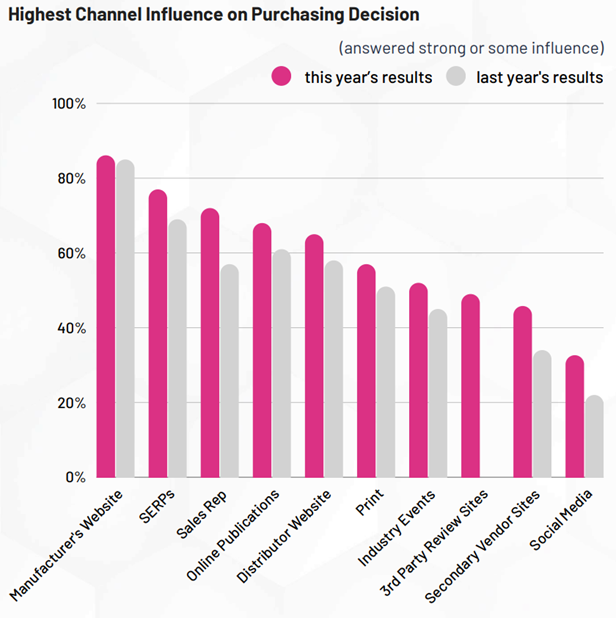
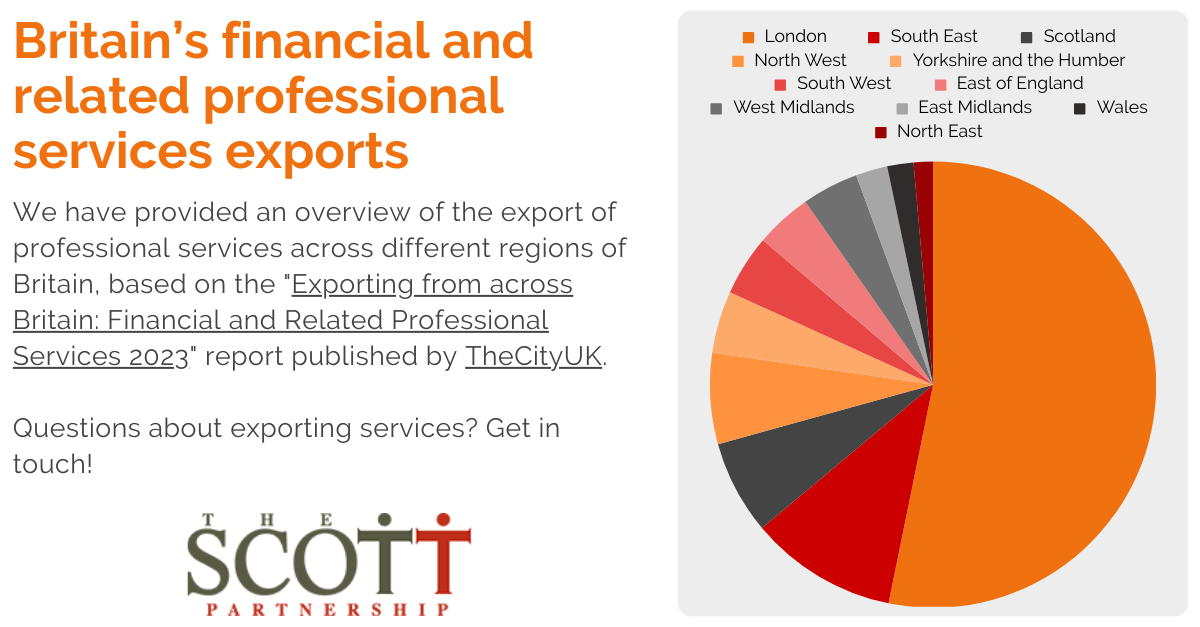
State of the industry - cell and gene therapy
Data taken from the Alliance for Regenerative Medicine (ARM) 2019 Cell & Gene State of the Industry Briefing report.
Cell and gene therapies are a rapidly growing sector in the field of regenerative medicine. The development of these therapies for clinical application to a wide range of human genetic disorders is now a reality, thanks to cutting-edge technology and commitment to addressing the logistical challenges of the supply chain. The market was valued at US$8 billion in 2018, and is projected to reach a value of US$12 billion by 2020, according to a Statista report.
These therapies aim to engineer damaged tissues and organs by stimulating the body’s own repair mechanisms, to heal previously irreparable damage. But what’s the difference between cell and gene therapies?
- Cell therapies involve the transplantation of cells and are a significant area of growth and potential for commercial development and patient access.
- Gene therapies use gene modification of cells to treat hereditary diseases in novel ways, or potentially prevent diseases like cancer.
The Alliance for Regenerative Medicine (ARM) held its annual briefing presenting the 2019 Cell & Gene Therapies State of the Industry in San Francisco in January – the largest cell and gene therapy-focused event of its kind – which drew in key stakeholder groups, including therapeutic developers, investors, and policymakers. Leading executives, life science media, patient advocates and academic leaders also attended, to further their understanding of key sector trends and metrics, recent advances and commercialisation challenges.
Global sector overview
Out of 906 regenerative medicine companies worldwide (including cell and gene therapies, and tissue engineering therapeutic developers), 484 are based in North America, 241 in Europe and Israel, 142 in Asia, 23 in the Oceania region, 15 in South America and one in Africa. Across these global sites of innovation, major therapeutic platforms and enabling technologies include:
- Smart biomaterials
- Tissue substitutes
- Advanced cells
- Cell-based immunotherapies
- Novel and synthetic gene delivery vehicles
- Genome editing
- Next-generation expression constructs
Clinical progress
The report confirms that clinical progress is on the increase, with eight product approvals in 2018, one gene therapy (LUXTURNA) and seven cell therapies (RECELL, Yescarta, Amniofix/EpiFix/EpiBurn, Kymriah and Alofisel). Additionally, by the end of the year, there were a total of 1,028 therapies in clinical trials, with 341 in Phase I, 595 in Phase II and 92 in Phase III. Out of this total, 362 were in gene therapy, 362 were gene-modified cell therapies, 263 were cell therapies and 41 were in tissue engineering (Fig 1).
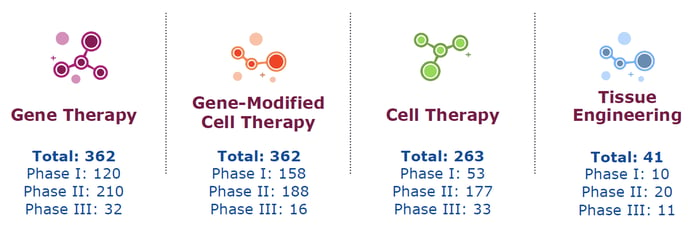
Figure 1: Total clinical trials by technology type, as of end of year 2018.
58% of all current regenerative medicine clinical trials are in oncology, 7% are in cardiovascular disorders and 6% are in musculoskeletal disorders (Fig 2).
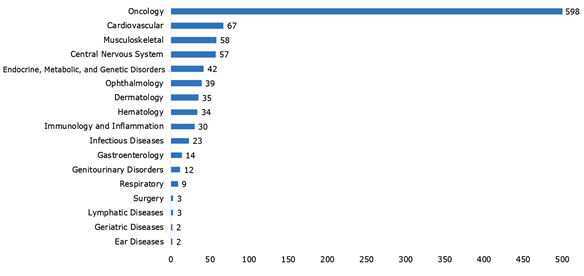
Figure 2: Number of clinical trials by therapeutic category. Source data provided by Informa.
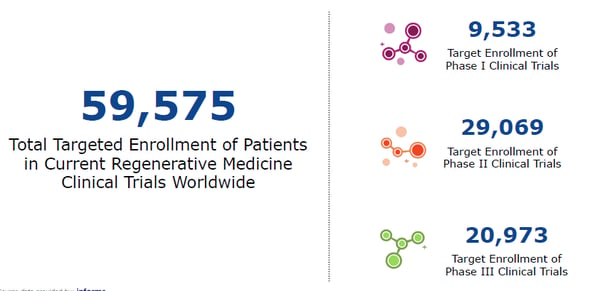
Figure 3: Patient impact of regenerative medicine. Source data provided by Informa.
Global financing in 2018
All financing for regenerative medicines increased from 2017 to 2018, but the greatest percentage increase came from initial public offerings (IPO), with a 659% increase year-on-year from 2017.
The total global financing for gene-based therapies, cell therapies and tissue engineering were up 73% from 2017 to 2018 ($13.3 billion). Gene-based and cell therapies were both up 64%, at $9.7 billion and $7.6 billion respectively, and tissue engineering saw the greatest growth in financing, up by 258% from 2017 to 2018 ($936.9 million). Total merger and acquisition transaction values were up significantly year-on-year, from $1,033 billion in 2016 to $20,042 billion in 2018 (Fig 4). These figures show that 2018 was a year of significant growth for regenerative medicine, which has also been marked by pronounced investor interest.
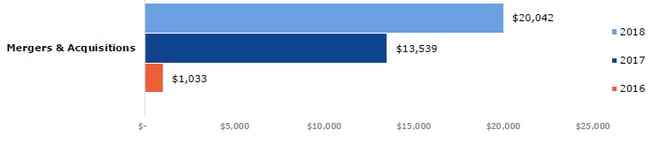
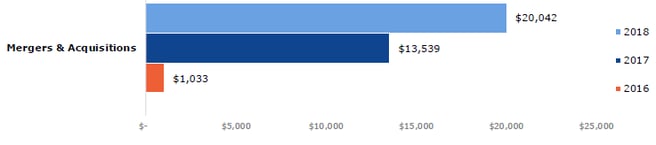
Figure 4: Total merger and acquisition transaction values, by year (US$ billion). Source data provided by Informa.
The future of cell and gene therapies
The creation of globally consistent regulatory policies facilitates the rapid and efficient development and introduction of regenerative medicine products across multiple markets worldwide. These internationally harmonised regulations benefit both manufacturers and patients. According to the ARM State of the Industry report, 2019 will see the sector address commercialisation challenges of regenerative medicines, including the development of new payment models. ARM plays an important role in innovating the reimbursement process – the way a healthcare provider is paid by private insurers or government payers – to accommodate advanced regenerative treatments. By facilitating collaboration with stakeholders and policymakers, ARM is helping healthcare systems to prepare for this new wave of novel therapies.
For more information on the Alliance of Regenerative Medicine, please visit https://alliancerm.org/. To access a copy of the report, click here.
If you would like to find out how we can help your organisation communicate its scientific offerings, please get in touch at business@scottpr.com or 01477 539 539.